CMMC is the abbreviated version of the term Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification. It is a United States Department of Defense initiative aimed at standardizing the readiness for cybersecurity processes all across the defence industrial base or DIB working under the federal government. This certification process or initiative was introduced as a means to measure the level of cybersecurity standards and incident response systems the defence contractors possessed. In this blog post, we will discuss CMMC Compliance Checklist, certification levels, and Federal Frameworks in detail.
As the contractors at the Defence Industrial Base deal with controlled unclassified information (CUI), it is essential to ensure that they meet the much-needed cybersecurity requirements. The consolidated process of security assessment through the understanding of the security frameworks of defence contractors is known as the CMMC.
The CMMC Compliance Checklist primarily focuses on the certification levels that a certain organization achieves through the improvement in the specific security framework applied for handling the controlled unclassified information or the CUI and federal contract information or FCI. As this information is vulnerable to cyber threats it is essential to ensure their security in the hands of the defence contractors.
The certification assessments apply to all types of defence contractors including both prime and subcontractors. Although according to the program, from 2026, some level of compliance process will be a necessity of any contract, contract requests will still be sent at lower levels of certification also.
CMMC compliance checklist, requirements and certification level
Various levels of CMMC Compliance: Details
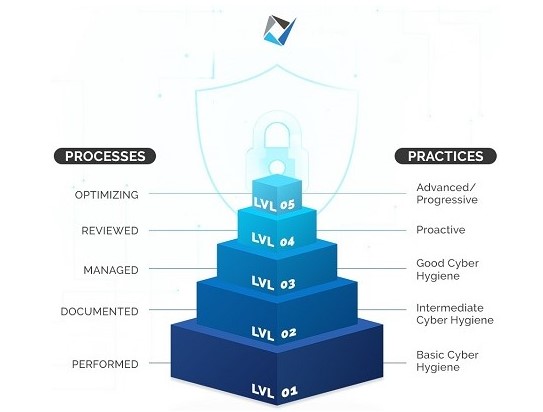
The CMMC Compliance Checklist is constituted of a range of mature capabilities that an organization needs to achieve to work in the Defense industrial sector. The process maturity that is required by every organization depends on the vulnerability of the external information systems that are put to use. These levels of maturity or certification levels can be categorized according to the increasing order of sensitive information tackled by the organization. The categorization can be done in the following manner:-
- CMMC Level 1
- CMMC Level 2
- CMMC Level 3
- CMMC Level 4
- CMMC Level 5
Apart from the above-mentioned levels or readiness assessment categories, a new maturity level has been introduced recently known as the CMMC 2.0.
The CMMC Levels can be enumerated as follows:-
CMMC Level 1
The CMMC Level 1 is the first on the certification levels within the framework. In other words, the organizations intending to get certified at this level need to perform certain cybersecurity practices. These practices need to be performed only in an ad-hoc manner which may or may not include the use of documentation. This is the reason why the extent of process maturity is not determined at this level.
The practices that form a part of this level generally encompass basic cyber hygiene. Level 1 is specifically designed for the protection of the Federal Contract Information or the FCI against cybersecurity threats. It consists of practices that are corresponding to the general security requirements that are specified in the 48 CFR 52.204-21. This implies that the basic security requirements demanded by this level are non-negotiable and need to be set right to achieve other cybersecurity maturity levels.
The CMMC Level 1 can be achieved by smaller companies and comprises a set of common security requirements that are universally accepted. As maturity in the cybersecurity processes is not expected at this level, the organizations applying at this level are not expected to deliver at that height.
CMMC Level 2
The CMMC Level 2 is more commonly referred to as a bridge to the next level. Generally, the second level of this government-led assessment is midway between the Level 1 certification and Level 3. But, certain situations related to compliance standards need to be addressed before the jump to Level 3 can be made which are dealt with at this level.
In comparison to the previous level, Level 2 places the organizations within the federal supply chains in a better position for defending the organizational information systems against dangerous cybersecurity threats. Along with the additional practices, this level also begins to include the process maturity component of the CMMC model.
CMMC Level 3
The level in the procedural maturity framework builds on the previous level. This implies that the level includes the Federal Acquisition Regulation or FAR practices and about twenty others that support cyber hygiene. The main emphasis of this level is to lay out the importance of planning and keeping up the cybersecurity efforts within an organization. The Level 3 clearance is required specifically for companies that create or have access to Controlled Unclassified Information.
In the general line of classification, the levels are created in the hierarchy of ‘Basic Hygiene’ to ‘Advanced or Progressive’. Concerning this categorization, Level 3 is considered as ‘Good Cyber Hygiene. The level includes all the requirements of the previous levels in addition to some others. These additional requirements are designed to focus on the planning, sourcing, and reviewing of the security policies and procedures implied by the contractor organizations.
CMMC Level 4
Level 4 of CMMC signifies a substantially proactive cybersecurity program. The organizations that successfully achieve this certification, depict the ability to adapt to the protective measures required during cyber threats. This allows the organizations to respond aptly to the changing methods, tactics, and procedures used during advanced persistent threats or APTs.
CMMC Level 5
The final level within the certification hierarchy consists of the CMMC Level 5. This level needs the defence organizations to standardize and optimize the implementing processes in an advanced manner across the whole organization. Building upon the practice approaches included in the previous level, this level focuses on the protection of Controlled Unclassified Information from Advanced Persistent Threats. Although the focus of the controls is not any different from the previous level, the additional controls and procedures help in delivering a deep and sophisticated cybersecurity framework within the certified organization.
Updates of CMMC 2. O:
The CMMC 2.0 is the new addition to the cybersecurity model of the Department of Defence. The new intermediate level streamlines all the requirements of the three levels of cybersecurity including the Foundational, Advanced, and Expert. The requirements at this level align with the requirements at each of these levels along with the widely accepted NIST standards of cybersecurity.
Understanding the CMMC Level required:
The Department of Defence contractors is not required to comply with the credentials of all the levels. Instead, specific contractors need to be certified in performing processes that adhere to the protection of the information they handle. For instance, a contractor that remains at the bottom of the supply chain needs to be certified in only Level 1 controls. On the other hand, contractors assigned the construction contracts of military bases need to be clarified at the highest level.
To determine the level of CMMC Certification a certain organization is required to have, it is essential to see where the Federal Contracts Information and the Controlled Unclassified Information are stored and how. After a readiness assessment has been completed, figuring out the required CMMC certification is quite simple.
Steps to completing the CMMC Compliance Checklist:
Certain steps are to be followed by defence contractors to create the CMMC Compliance Checklist. These steps or processes can be explained in the following manner:-
Assessing the CUI of the organization –
The first and most crucial part of creating the checklist is to understand the type of information tackled by the organization. After this, the information that falls under the purview of CMMC has to be segregated. The assessment checklist is designed to cover the controlled unclassified information (CUI) within the non-federated IT systems. The CMMC has its focus on the CUI within the non-federal systems across the defence organizations. This difference is very crucial in the sense that certain organizations having FedRAMP and FISMA certifications still have CUI that require CMMC self-assessment.
This makes the certification assessment of organizations crucial. A clear understanding of the kind of data used by organizations and bringing it under the compliance process before submitting the CMMC Certification is necessary.
Leveraging other Federal Frameworks
The possibility of the CMMC reciprocating with other federal frameworks is under discussion. The organizations seeking to achieve the CMMC certification should begin to attempt at leveraging the existing frameworks. Certain other certifications could make the process of achieving CMMC certification easier. Some of these are:-
- ISO 27001 – This is an international framework that focuses on managing information through some best practices and industry standards.
- NIST 800-171 gap assessment – It is a special publication that provides the guidelines that can be followed in managing the CUI in non-federal information systems.
- Risk management framework – This is a part of the NIST, the Risk Management Framework helps the organizations to access controls, and implement various processes including dissemination controls and control communications for managing the risk while handling data in external information systems.

Reading the CMMC Appendices and Assessment guides
The Department of Defence has been consistent with its changing framework and appendices. The review and updating of these documents are one of the special parts of completing the CMMC Compliance Checklist. In addition to this, the CMMC has provided an assessment guide that explains the five levels of capability requirement for the CMMC Certification.
Completing the NIST 800-171 gap assessment
Besides the CMMC, another publication points out the use of the Controlled Unclassified Information within the non-federal information systems. This publication is abbreviated as NIST SP 800-171. This publication is very helpful in situations where an organization is seeking to get a new contract or become CMMC certified or both.
Seeking out the right partners
The final yet crucial step in the complete process is to get the CMMC Certification through certified third-party partners. Many certifications pursued by an organization have the potential to interact with CMMC in several ways. In such situations, a right third-party CMMC partner will help pursue a smart strategy that addresses the compliance needs and goals of the specific organization.
Importance of CMMC model in the cybersecurity for DOD contractors:
The CMMC is best described as a new cybersecurity standard that has been introduced for the contractors working under the Department of Defence. The CMMC Certification is focused on ensuring that all the defence contractors have enough control over both the internal network as well as unclassified networks, to protect the sensitive data from persistent threats. In a certain way, it can be considered that the CMMC was applied because several contractors had failed in implementing the self-assessment models.
This subsequently had led to several breaches of high-profile defence contractors. The CMMC compliance checklist ensures that the certified organizations are successful in maintaining concise documentation of the use of CUI. In addition to this, the certification practices help the contractors in performing proper asset management while adhering to government-wide policies on intellectual property.
FCI and CUI: Meaning and difference between the two
The term FCI is the abbreviated form of Federal Contract Information and CUI is the abbreviation of Controlled Unclassified Information. According to the definition, FCI signifies the information that is given or generated by a government contractor for product delivery along the contractual period. In simple words, the FCI is not meant to be out in public or for any public use. On the other hand, the CUI refers to the information that is created or possessed by a government entity.
This kind of information requires certain safeguards like law, regulation, policy, or permit for the dissemination controls and accessing them. Although theoretically, both these kinds of information are similar, there is a significant difference between the two. While both this information is government-generated or possessed, FCI is not meant for public use and the CUI requires a lot of security certifications to be used. Thus, while all FCI is not CUI, all the CUI that a government contractor possesses is FCI.
FedRAMP Certification: Explanation
The term FedRAMP stands for Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program. This is the standardized security assessment process designed for cloud-based products and services used by Federal agencies in the U.S. The primary focus is to keep the federated data in the cloud amidst high-level security. As the confidential information that is kept in the cloud requires the highest level of security, receiving the FedRAMP authorization is very difficult.
The level of security for such information is provided by law as it is a question of national security. There exist 14 applicable laws and regulations along with the 19 standards and guidance documents. In simple words, this is one of the toughest software-as-a-service certifications provided in the world.
Microsoft Product Placement for CMMC:
The Microsoft Product Placemat for CMMC is an interactive format in which Microsoft expresses how the cloud-based products and services provided by them meet the security requirements for CMMC certification. There exists a default view that gives an illustration of the practices with Microsoft coverage which are inherited from the cloud platform. In addition to this, it also provides shared coverage which is again inherited from the cloud.
This process allows the user organization to go deeper into every practice and recognize the details related to inheritance and receive prescriptive guidance for taking actions and meeting the compliance requirements.
GAP Analysis and CMMC Mock Assessment test: Benefits
The CMMC Gap Analysis is a method of understanding and recognizing the controls required for meeting the CMMC Compliance Checklist. It additionally provides recommendations on certain approaches that help in mitigating the issues in the business processes. The benefits of this process can be stated as follows:-
- Understanding the level to which the organizational standards meet the needs of NIST 800-171 gap assessment.
- Satisfaction of timely compliance with CMMC standards.
- Familiarity with assessment methods.
- Provides proof to shareholders and prospective clients that the company can meet security standards.
- Organizations can win better and more lucrative projects.
EPC Group: A CMMC Compliance Perspective
The EPC Group is a leading Managed Security Services Provider in the U.S. The experience this organization has in implementing cybersecurity measures, accessing the maturity standards, and applying the government guidelines, makes them incomparable. This makes the company a go-to third-party assessor that initiates the CMMC Consulting and certification procedure. Additionally, the EPC Group has the required technical expertise in the field to conduct readiness assessments and perform a gap analysis.










