Microsoft Azure’s infrastructure incorporates a feature known as paired regions, providing a robust geographical redundancy solution to safeguard customer data and services.
This design approach ensures business continuity, even during large-scale events like natural disasters, widespread network failures, or power outages.
A paired region comprises two specific Azure regions linked within a larger geographical area. For instance, ‘West US 2’ and ‘West Central US’ form a pair in the United States.
By providing data resilience across geographically proximate yet distinct data centers, Azure ensures that at least one region is available during region-wide events, fostering high availability and fault tolerance.
What are Azure Paired Regions?
In a paired region configuration, one region is labeled as the ‘primary’ region and the other as the ‘secondary’ region. These two regions are directly connected through a low-latency, high-bandwidth network link, resulting in faster data replication and synchronization between the paired regions.
In a paired region setup, Microsoft commits to ensuring that at least one region in each pair will be available during a significant event impacting service availability.
The primary reason for pairing regions is to allow for data redundancy, high availability, disaster recovery, and isolated updates. Each Azure region within a pair operates independently but coordinates with its partner regarding planned system updates and data replication. The purpose of region pairing is to provide enhanced resilience and high availability for applications and services deployed in Azure.
The following are some examples of Azure Region Pairs:
| Geography | Regional Pair A | Regional Pair B |
| Asia-Pacific | East Asia (Hong Kong) | Southeast Asia (Singapore) |
| Australia | Australia East | Australia Southeast |
| Australia | Australia Central | Australia Central 2* |
| Brazil | Brazil South | South Central US |
| Brazil | Brazil Southeast* | Brazil South |
| Canada | Canada Central | Canada East |
| China | China North | China East |
| China | China North 2 | China East 2 |
| China | China North 3 | China East 3* |
| Europe | North Europe (Ireland) | West Europe (Netherlands) |
| France | France Central | France South* |
| Germany | Germany West Central | Germany North* |
| India | Central India | South India |
| India | West India | South India |
| Japan | Japan East | Japan West |
| Korea | Korea Central | Korea South* |
| North America | East US | West US |
| North America | East US 2 | Central US |
| North America | North Central US | South Central US |
| North America | West US 2 | West Central US |
| North America | West US 3 | East US |
| Norway | Norway East | Norway West* |
| South Africa | South Africa North | South Africa West* |
| Sweden | Sweden Central | Sweden South* |
| Switzerland | Switzerland North | Switzerland West* |
| UK | UK West | UK South |
| United Arab Emirates | UAE North | UAE Central* |
| US Department of Defense | US DoD East* | US DoD Central* |
| US Government | US Gov Arizona* | US Gov Texas* |
| US Government | US Gov Virginia* | US Gov Texas* |
Certain geographical areas are subject to access restrictions to enable tailored client solutions, such as localized disaster recovery. Access to these zones can be granted only via a specific support request.
Here are a couple of notes about the region pairs listed in the table:
- West India’s failover region is one-way directed.
- While South India serves as the failover region for West India, Central India acts as the failover region for South India.
- Brazil South stands out as its failover region, South Central US, which lies outside its geographical boundary.
- Conversely, South Central US’s failover region is not Brazil South.
Benefits of Using Azure Paired Regions
Azure Paired Regions offer several technical advantages, primarily related to high availability, disaster recovery, and data sovereignty. The following outlines these benefits in detail:
- Disaster Recovery and High Availability: Paired regions ensure that at least one region remains functional in the event of large-scale network or infrastructure failures. It allows organizations to create highly available applications and provides a quick recovery path during disasters.
- Data Sovereignty Compliance: The paired region design ensures that data replicated across regions remains within the same geopolitical boundary. This adherence assists in complying with data sovereignty laws and regulations that mandate data residency within specific jurisdictions.
- Region Isolation: The paired regions are physically isolated from each other to minimize the risk of simultaneous impact due to a single disaster. They are intentionally located in different seismic and flood zones and are typically distanced by a minimum of 300 miles.
- Sequential Update Rollouts: Azure sequentially conducts planned maintenance activities on paired regions to avoid concurrent downtime. This approach ensures that at least one region is always operational during these events.
- Platform-Managed Replication: Several Azure services, like Azure Storage and SQL Database, offer automatic geo-replication to the paired region. This feature simplifies the management of disaster recovery mechanisms.
- Controlled Feature Rollouts: Azure releases updates or new features sequentially to the regions within a pair. This method allows for thorough testing and minimizes the risk of simultaneous potential disruption across both regions.
Availability Zones & Geography Size Considerations
The concepts of Availability Zones and Geographical Size have significant implications in the Azure infrastructure. Here is a detailed explanation of both and their influence on Azure Paired Regions.
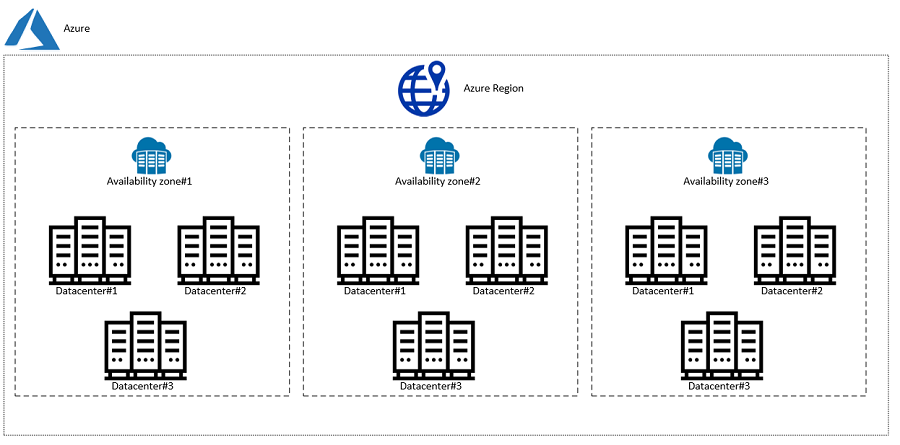
Availability Zones
Azure Availability Zones are unique physical locations within an Azure region, each equipped with its power, cooling, and networking. They are designed to protect applications and data from data center failures. Within an Azure Paired Region, using Availability Zones further strengthens fault tolerance and ensures high availability. By deploying resources across Zones within a region, users can protect their applications and data from the failure of a single data center. If a zone becomes unavailable, the traffic can be directed to another zone within the same region.
Geography Size Considerations
Geography in Azure refers to a discrete market, typically containing two or more regions, that preserves data residency and compliance boundaries. When selecting regions for a pair, it’s important to consider geography size because data transfer speeds can impact application performance and synchronization times. However, the region pairs are set by Azure, ensuring data residency within the same geopolitical boundary.
Geographic Size Considerations When Choosing a Region Pairing
The size of a region can significantly influence the outcomes of the pairing, especially when considering parameters such as population density, resource allocation, infrastructure development, and logistical considerations. Disparities in size can lead to skewed comparisons or imbalances in resource distribution, which might yield different outcomes.
Key considerations include:
- Population Density: Larger regions may have a higher population density, which can affect factors such as traffic, resource usage, and public service requirements.
- Resource Allocation: A region’s geographic size can influence resource distribution. Smaller regions may require fewer resources for infrastructure and services, while more significant regions may necessitate more.
- Infrastructure Development: Larger regions may have more developed infrastructure due to the greater area covered, whereas smaller regions may be less developed.
- Logistical Considerations: The geographic size of a region can impact logistics. More significant regions may pose challenges in transportation and delivery of services, while smaller regions may be easier to manage.
- Data Comparability: If regions are being paired for comparative studies, significant differences in size may lead to skewed data or unbalanced comparisons. Hence, pairing regions of similar sizes or accounting for size differences in data analysis is crucial.
Availability Zone Considerations When Choosing a Region Pairing
They refer to distinct locations within a cloud region, each designed to be isolated from failures in other zones, thus providing redundancy and resilience. Pairing regions with an unequal number or distribution of availability zones may affect distributed applications and services’ reliability, performance, and cost-efficiency.
Key considerations include:
- Resilience and Redundancy: Regions with multiple availability zones can provide better fault tolerance, as a failure in one zone can be mitigated by shifting load to another zone in the same region.
- Performance: If a region has more availability zones, it can offer better performance by spreading the load across these zones, thus reducing the likelihood of any zone becoming a performance bottleneck.
- Disaster Recovery: In a disaster scenario, regions with more availability zones can provide more options for recovery, thereby minimizing downtime.
- Cost Efficiency: The distribution of resources across availability zones may impact costs. For example, data transfer between availability zones within the same region can be less expensive than inter-region data transfer.
- Data Sovereignty and Compliance: Some regions may have specific legal and regulatory requirements for data sovereignty.
Is EPC Group Your Solution for Microsoft Azure Consulting Services?
By partnering with us, you get access to a broad range of services crucial for leveraging Azure’s potential to its fullest. A noteworthy aspect is our expertise in Azure region pairing, which is integral to implementing disaster recovery strategies, data replication, and availability.
Region pairing in Azure refers to the linkage of two regions for resource redundancy and disaster recovery. Our extensive experience will assist you in optimally configuring and managing region pairing. We will ensure that resources are correctly and efficiently replicated to the paired region, thereby maintaining high availability and minimizing the possibility of data loss.
Our Azure consultation services encompass many other offerings, including architecture design and implementation, application migration, data management, analytics, security, and compliance.
Our highly skilled consultants work closely with you, understanding your business needs and technical requirements to provide customized Azure solutions. By choosing EPC Group as your Azure consulting partner, you can harness the power of Azure to drive innovation, achieve cost-efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in the marketplace.










