The CMMC Compliance model is representative of the certification program designed by the Department of Defense for protecting vulnerable federal data from persistent threats. The program ensures that the organizations working within the Defense Industrial Base sector are ready to combat and protect the data within the non-federal information systems from cybersecurity threats. Moreover, in this blog post, we will dive into details about the CMMC Audit process.
The focus of this CMMC certification process is to primarily protect two kinds of data namely: Federal Contract Information or FCI and Controlled Unclassified Information or CUI. The Defense industry is one of the most threat-prone industries in the market which in turn requires a strong security framework for protecting the constituent information. The CMMC has been introduced for decreasing this risk of continuous threat while creating a unified Department of Defense standard for cybersecurity.
The requirement for CMMC certification is changing the market landscape for all companies acting as contractors or subcontractors across the globe. For completing the certification process successfully, a third-party CMMC Consulting organization will have to be contracted by the aspiring organization to become CMMC Compliant.
Requirement for a CMMC Audit: An organizational perspective
According to the U.S Department of Defense, all the organizations working within the defence industrial base would require some form of CMMC Audit and Certification in place. This regulation falls at par with the fact that by 2026, all active contracts given out by the DOD would demand a specified level of CMMC Certification from the organizations. Although this regulation has led to massive changes in the market environment, organizations that act upon complying with CMMC Compliance requirements will be an advantage over other competitors.
As all the new and existing defence contracts would at some time go to CMMC Compliant organizations, the early adopters of the regulation would have a competitive edge over the others. But, competitive advantage is not the only benefit of adopting the CMMC regulation. Apart from this, the certified organizations would have to face a lesser risk of financial loss in the face of cybersecurity breaches. As the government can impose heavy fines on the defence contractors post data breaches, organizations with the certification would have an additional level of security against persistent threats.
Read More – CMMC Compliance Checklist Guide
CMMC Certification levels: Understanding the best CMMC Level for an organization
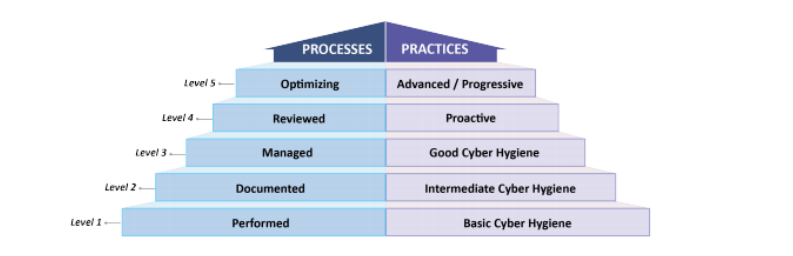
The CMMC Certification process is a five-level model. It is a cumulative model whereby each of the levels has different practices and processes which have been specified separately. The levels range from ‘Basic cyber hygiene’ to ‘optimizing cybersecurity’ at the last level. As a defence contractor advances to a higher level of the model, it indicates a higher level of protection to the sensitive information being processed in the non-federal information systems. The various levels of the model can be enumerated in the following way:-
- CMMC Level 1 – This is designed to safeguard the Federal Contract Information or FCI.
- CMMC Level 2 – This is a transitional step in cybersecurity practices that help in protecting Controlled Unclassified Information or CUI.
- CMMC Level 3 – This level is designed to protect the CUI completely.
- CMMC Levels 4 and 5 – These final levels help in protecting the CUI and reducing the risk of advanced persistent threats.
Duties of a CMMC Auditor:
The CMMC Audit is conducted by an authorized CMMC Auditor. The Auditor has the power of performing several types of audits depending on the CMMC maturity level that has been applied for by the organization. As the process is overly complicated, the involvement of the contractor may vary depending on the fact that multiple audits may have to be performed.
Certain assessors candidates the contractors in the process of achieving the certification of CMMC. The Auditors tend to be meticulous in their job and in stating the requirements an organization needs to achieve the certification level intended. The function of a CMMC Auditor does not differ much from the traditional Auditor, except for the fact that the CMMC model itself demands third-party certification. But, the CMMC Auditor cannot provide that certification unless he is authorized to do so.
Thus, these Auditors can help the interested organizations by performing the following:-
- Checking the Data – The CMMC Auditor knows the CMMC model and can inform the organization about the form of data being processed by them. This is a crucial piece of information as this determines the correct level of a maturity level to be applied for.
- Checking the cyber hygiene – Also known as cyber resilience, a CMMC Auditor is required to check the cyber health of the organization. Without this check, it is difficult to implement the controls of the maturity level.
- Staff awareness check – Auditors are additionally required to assess whether training programs within the staff have been initiated and check the levels of cybersecurity awareness the staff of the organization possesses.
- Domain Audit – The process of checking whether the domains needed for the certification are present in the interested organization is also one of the duties of an Auditor.
- Audit of the process integration – The final step of the audit process is to test and determine the extent to which the cybersecurity capabilities have been incorporated within the organization. This test would help in deciding whether the company has reached the required level of maturity.
Process of preparing for a CMMC Audit:
The CMMC certification includes a five-level maturity model which varies based on the type of information being tackled by the defence contractors. The first level deals mainly with the security of the sensitive information termed as the Federal Contact Information or FCI. The next two levels help in protecting the Contract Unclassified Information or CUI. Finally, the last two levels help in creating a security framework against advanced cybersecurity threats.
The CMMC capabilities can be categorized across 17 domains. Some of these include risk management, situational awareness, and the capabilities related to incidence response. But, the process of achieving the CMMC Certification can be quite complicated.
The process of preparing for this certification can follow the below-mentioned methods:-
- Determining the maturity level of the organization – The defence contractors can determine their CMMC level of maturity by defining their use of data and recognizing the amount of FCI and CUI within their network. In addition to this, the security levels and methods employed for the protection of such data also has to be assessed.
- Taking the NIST 800-171 self-assessment – The NIST 800-171 forms an integral part of the CMMC audit. This code provides for a range of regulations and guidelines that the Non-federal entities are required to follow while storing, processing or transmitting the CUI and the other security systems. A self-assessment report based on this code needs to be submitted before the CMMC audit are performed.
- Creating the SSP & POA&M – Before involving in the CMMC Certification process, the interested organisation is required to build a System Security Plan or SSP and Plan of Actions and Milestones or POA&M.
- Reporting the score to the SPRS – In the next step of preparation, the defence contractors need to submit their assessment score, their SSP and POA&M to the Supplier Performance Risk System.
- Working in collaboration with CMMC Consultant – To ensure that all the preparatory steps of the CMMC self-assessment process are completed properly, contractors work in collaboration with CMMC Consultants.
Developing an SSP & POA&M:
The term SSP refers to System Security Plan which is an explanatory document which is designed for updating the substantial changes made by the defense contractors, across their security systems. All the crucial changes or remediation needs to be recorded in the Plan. To clear the NIST 800-171 self-assessment procedure successfully, the organization needs to create the SSP in a manner that records the crucial information related to all systems across the company.
This information is required to include the processes in which the CUI is stored, used, or transmitted. On the other hand, the term POA&M stands for Plans of Action and Milestones. In simple terms, this can be considered as a to-do list. This document states the weaknesses of the organizations and a plan of action through which that weakness is meant and a milestone is met. While the SSP is a descriptive document, the POA&M should be concise. The designing of these documents is necessary for clearing the NIST 800-171 self-assessment.
EPC Group as the CMMC Consulting partner:

EPC Group is one of the most popular Managed Security Services Providers in the U.S. This organization has a wide range of experience in implementing various cybersecurity measures accessing the maturity standards and applying government guidelines. This quality makes this organization valuable and an incomparable CMMC Consultant. The company has emerged to be the go-to third-party assessor that initiates the CMMC audit and certification procedure.
Along with this, the EPC Group has the required technical expertise in the field of conducting readiness assessments and performing gap analysis. In addition to helping through the compliance procedure, the Group will help the organizations in maintaining a CMMC compliant environment by monitoring, detecting, and reporting cybersecurity crimes in a constantly evolving technological environment. This gives the client organizations a scope to address their vulnerabilities and update the presently operating security plan. Also, the EPC Group helps their clients in scheduling the CMMC audit through a certified 3PAO










