In the contemporary business environment, organizations are increasingly demanding services that are capable of providing self-service models. As executives continue to strive toward deriving the maximum value out of the tech infrastructure, Power BI Embedded continues to gain much-needed popularity.
Power BI Embedded Analytics refers to a premium feature of Power BI service that allows the user organizations to use the Power BI Embedded API to their advantage. This would help these companies to embed the Power BI reports from their workspace to a web page or a custom application.
As the service is a part of Microsoft Azure, it empowers the users to share meaningful yet interactive dashboards and reports with the customers, employees, and other areas where the data is required to be consumed.
Benefits of Power BI Embedded:
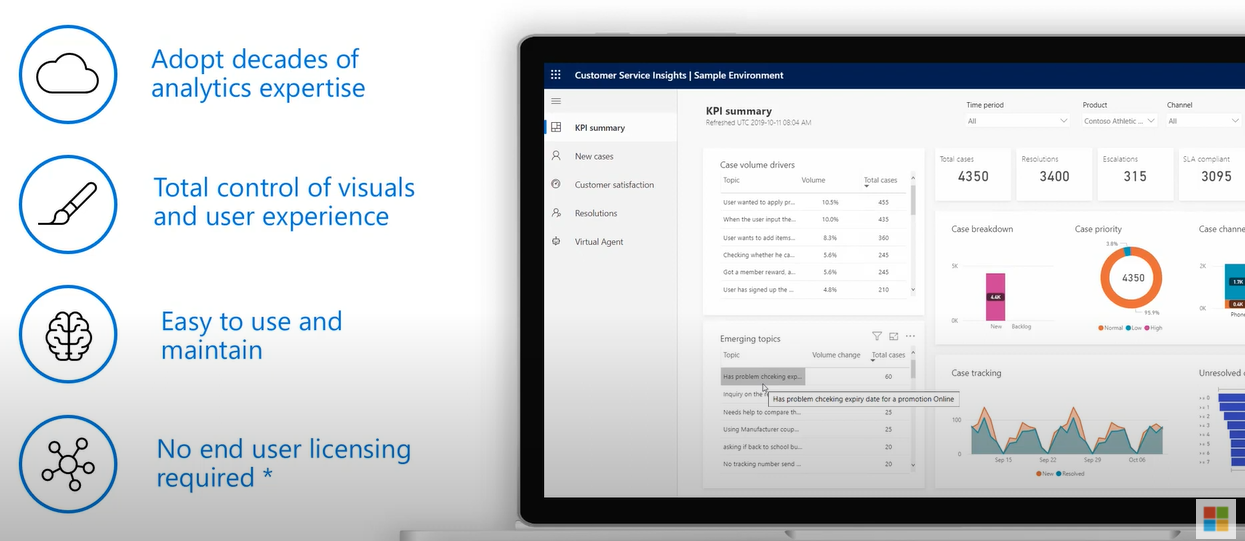
The benefits of the Power BI Embedded service can be enumerated in the following manner:-
- The service enables the users to share the content of the Power BI workspace both within the organization and outside without the need for any extra licensing.
- It permits the company to define and manage the user experience according to the audience.
- The filtration of the data based on user identity is another benefit of the service.
- The service ensures that the end-users receive a stable experience that does not differ every month nor does it need any monthly training.
- It provides flexible navigation and reduces the need for training and costs.
In addition to this, the Power BI Embedded Gen2, which is still in preview, promises improved tools and features for scaling, better performance, and simpler access to paginated reports and AI features.
Type of solutions available with Power BI Embedded Analytics:
Power BI Embedded Analytics consists of two distinct kinds of solutions that have different fields of use. The service can be categorized into:-
- Embed for your customers and
- Embed for your organization
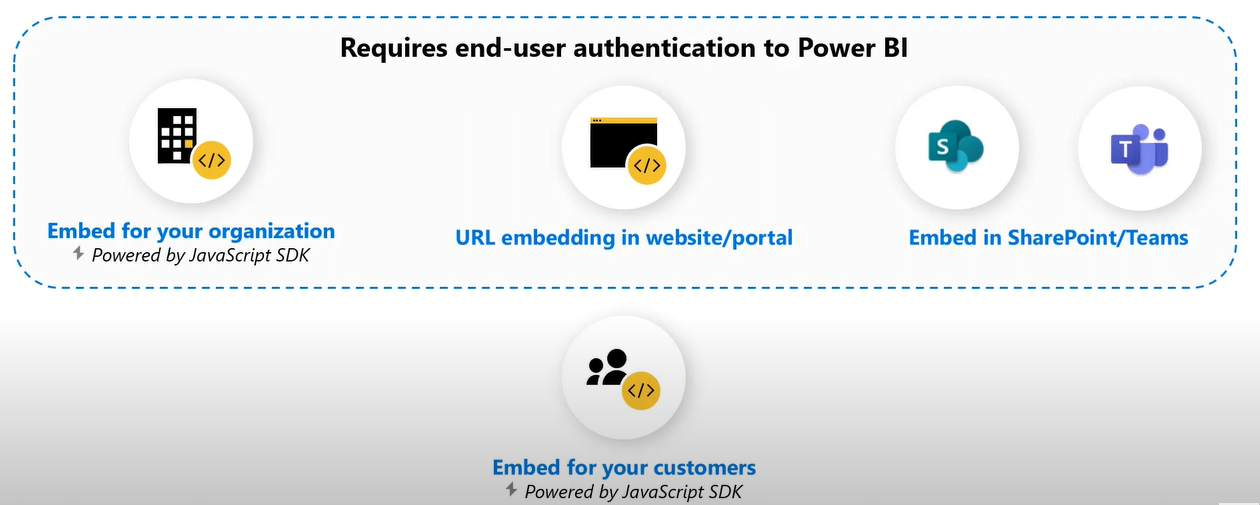
The term Embed for your customers implies that the solution permits the user company to build an application that uses mon-interactive authentication against Power BI. The customers of user companies are generally considered external users who would not need to sign in separately for using the Power BI credentials for viewing the content of the embedded report.
In general, the embed for your customer’s solution is used by independent software vendors or ISVs that develop applications for third parties.
On the other hand, the embed for your organization solution allows the user organization to build applications that require signing in with the Power BI credentials. After signing in, the users can specifically consume the embedded content that is accessible to them within the Power BI service. This solution is at large used by organizations that build applications for their internal users with the company’s framework.
Power BI Capacities: Meaning
The term Capacity within Power BI refers to a collection of resources that are reserved for exclusive use in certain fields. These capacities enable the user companies to publish the reports, dashboards, and datasets of the users in a hassle-free manner.
The process of publishing these reports and datasets does not even require a per-user license. This set of resources also provides a dependable and consistent performance of the user company’s content.
Power BI Embedded Analytics service provides users with two kinds of offerings that include Power BI Embedded and Embedding with Power BI. While Power BI Embedded is part of the Azure offering that requires A SKUs, Embedding with Power BI is an offering of Power BI Premium that requires P or EM SKUs. The Power BI Embedded is associated with the solution termed as embed for your customer.
Capacities and SKUs: An Overview
While Capacity refers to a set of resources reserved for exclusive use, the term SKUs is not used in isolation. This implies that SKUs can be categorized into certain types which include the A SKUs, P SKUs, and EM SKUs. The phrase SKUs refer to a Platform as a service that is available with a set of APIs used by independent software vendors or ISVs.
Every Capacity is designed to offer a range of SKUs and each of these SKUs provides different resource tiers for memory storage or computing. The type of SKU required by a user organization depends on the type of solution the company wishes to deploy. Power BI Embedded is provided with an A SKU while Power BI Premium offers both P and EM SKUs.
Also read – Power BI Embedded Consulting
The following table explains certain scenarios, the capacity required in the scenarios, and the specific SKUs needed for each one of them.
| Scenario | Azure ( A SKU) | Office (P and EM SKUs) |
| Embed for your customers (app owns the data) | Can be used | Can be used |
| Embed for your organization (user owns the data) | Cannot be used | Can be used |
| Microsoft 365 apps | Cannot be used | Can be used |
| Securing URL embedding | Cannot be used | Can be used |
Kinds of Capacities available with Power BI:
The various kinds of SKUs available within Power BI can be categorized as A SKUs, P SKUs, and EM SKUs. While moving to production, Power BI Embedded Analytics is required to use one or more of these capacities for publishing the Power BI content.
The various kinds of capacity SKUs, their entry levels, and pricing structures can be categorized as follows:-
- A SKUs
| Name | Virtual Cores | Memory (GB) | Peak renders/ hour | Cost/hour |
| A1 | 1 | 3 | 300 | $1 |
| A2 | 2 | 5 | 600 | $2 |
| A3 | 4 | 10 | 1200 | $4 |
| A4 | 8 | 25 | 2400 | $8 |
| A5 | 16 | 50 | 4800 | $16 |
| A6 | 32 | 100 | 9600 | $32 |
- P SKUs –
| Name | Virtual Cores | Memory (GB) | Peak renders/hour | Cost |
| P1 | 8 | 25 | 2400 | $4995/mo |
| P2 | 16 | 50 | 4800 | $9995/mo |
| P3 | 32 | 100 | 9600 | $19995/mo |
- EM SKUs –
| Name | Virtual cores | Memory (GB) | Peak renders/hour | Cost |
| EM1 | 1 | 3 | 1-300 | $625/mo |
| EM2 | 2 | 5 | 301-600 | $1245/mo |
| EM3 | 4 | 10 | 601-1200 | $2495/mo |
Understanding the amount of capacity needed by an organization:

The process of calculating the kind of capacity required for the deployment of Power BI Embedded Analytics within a user organization is quite complicated. The reason for this complication is the fact that the process takes into account several parameters, some of which are difficult to predict.
Certain scenarios that need to be taken into account while calculating the capacity include –
- The data models used by the company
- The number and extent of complexity of the required queries
- The distribution of the usage of an application on an hourly basis
- Rates at which data is refreshed and
- Additional usage patterns that are difficult to predict.
To make the process of capacity calculation simpler, the Power BI Capacity Load Assessment Tool has been designed. The tool was designed to understand the extent to which the capacity of a user organization can handle certain workloads. It uses PowerShell to generate automated load tests against the capacities of the user company. After this, the user is permitted to choose the reports they wish to test and the number of concurrent users that can be simulated. But, the users should be mindful of the existing load handled by their capacity. Additionally, it should be kept in mind that load tests should not be run during top usage hours.










